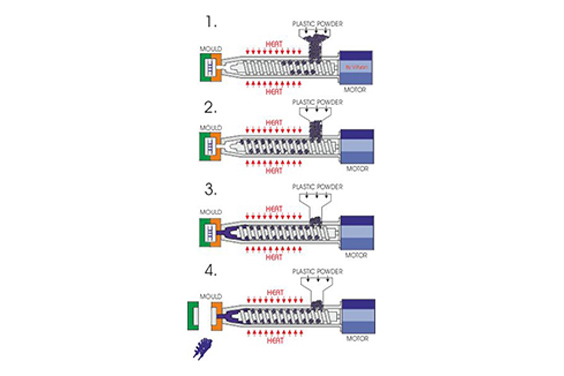
Thermosetting materials are one of the plastic molding tools used in making items that are applicable to numerous industries, including micro molding companies. There are several types and their applications vary.
In this post, we will discuss the various types of thermosetting plastic, their application, and so many more. But before that, let’s get a full understanding of what a thermosetting material is.
What is a Thermosetting Material

A thermosetting material (alternatively known as thermosets, thermosetting resin, or thermosetting polymer) is a normal liquid material that hardens irreversibly when heated. Thermosets have high melting points, but they get solid after being exposed to a level of heat. However, once they are hardened, they can’t be remolded or liquefied anymore.
Also, the melting points of thermosetting materials are different. Some have extremely high melting points, while others have a less-higher melting point. In cases where they are overheated, they disintegrate and get disfigured. This is why delicate and medical molding processes, such as medical plastic injection, insert molding, and medical overmolding injection molding rely on thermosetting materials‘ behavior.
When a thermosetting material is poured into a mold and heated, it solidifies into the specified shape. But while this is going on, cross-links that keep the molecules intact and modify the thermosetting material’s basic nature, which prevents it from melting, are produced. In many circumstances, introducing a catalyst or exerting external pressure can speed up the cross-linking process.
What are the Types of Thermosetting Plastic Materials
There are several types of thermosetting plastic materials and each of them have their distinct features and applications. Below are the most common types of thermosetting plastic materials.

Vulcanized Rubber
This type of rubber is more hardened than natural rubber. Once it solidifies, it can’t be recycled. It’s used in the production of several goods as it has both electrical and thermal insulation characteristics. It also has good abrasion properties and it’s not expensive.
Vulcanized rubber is used to make automobile tires because of its high tensile strength, which decreases the risk of tire punctures. It is also used by insert molding suppliers to shield metal and iron items.
Bakelite
It is used in the fabrication of a variety of products because it is easily moldable in its liquid condition. Bakelite also has electrical insulating qualities, which makes it commonly applicable in the electrical industry for switches, boards, sockets, and wire insulation.
It also has the unique quality of being able to be manufactured in various colors, which is why it is commonly used in the production of colored bangles, bracelets, and artificial jewelry. You can also find it in a variety of kitchenware products.
Duroplast
This is a composite thermoset material that’s similar to Bakelite, but with the addition of cotton or wool fibers for reinforcement. Duroplast is lightweight and sturdy, which is one of its most important features. This is why it’s used to make automobile bodies, which in turn lowers the cost of steel used in making car parts. It is also commonly used in the production of toilet seats.
However, it has a significant drawback – it can’t be decomposed easily. And if it is burnt, highly toxic vapors will be released, and these are hazardous to the environment.
Urea-Formaldehyde
As the name implies, it’s a thermosetting material made from the reaction between Urea and Formaldehyde in the presence of water and at a PH greater than 7. This thermosetting material has a semi-crystalline structure and is excessively cross-linked. It becomes solid immediately when the heat temperature is raised.
Urea-Formaldehyde is commonly used in the wood products industries and it’s also used as particle board adhesive. Laminating decorative goods, coating air filtration, and fiberglass matting are some of its other applications.
Melamine-Formaldehyde
It is made from the combination of Melamine and Formaldehyde in a low alkaline condition. Just like Urea-Formaldehyde, this material is commonly used in the wood products industries. Melamine polished boards outperform natural boards in terms of heat and chemical resistance.
Melamine resins are fire-retardant, which makes them applicable as additives in the production of papers, paints, plastics, and flame-resistant fabrics. Other products they are used for are particleboards, laminates, cockware, and floor tiles.
Epoxy
This is a reactive thermosetting resin. It is capable of resisting heat and corrosion which is why it is commonly used in the aerospace industry. Epoxy resin is also used in structural adhesives, covering electrical components, and metal coatings.
Cyanate Ester
It outperforms Epoxy in terms of water absorption, dielectric loss, and high-temperature stability. Cyanate Ester is often brittle, which is why it is frequently combined with Epoxy or other thermosetting materials to produce better-toughened products with improved features. Because of its superior structural and mechanical qualities, it is used in the aerospace industry. It’s also used for electronic chip adhesives and encapsulating various electrical devices.
Polyimide
This thermosetting material has good thermal and chemical properties, and it can withstand high temperatures. Because of its great mechanical strength and water resistance, it is commonly used in the manufacture of sockets, bushings, and bearings.
Silicone
Silicone resin has a strong 3D network structure, which makes it applicable in several sectors. Silicone injection molding provides strong, heat and water coatings with excellent dielectric characteristics. Also, it can make films that are resistant to sunlight.
This thermoset comes in a variety of textures, ranging from highly viscous liquids to solids. It is also reliable and durable, which is why it is used in art, coatings, sealants, silicone fluids, and the electrical industry. Because of its biocompatibility, medical molding manufacturers prefer it in making medical equipment.
Polyurethane
Polyurethane has a strong foam structure that is capable of insulating various materials. Examples of these materials are steering wheels, gaskets, car bumpers, windshields, door panels, and any other automotive and electrical parts. The bad side of this resin is that it’s susceptible to microbial infections and it frequently turns yellow when exposed to sunlight.
Furan
It is highly volatile with boiling temperatures almost at room temperature, and it can be dissolved in organic solvents, such as ether, acetone, and alcohol. Furan is commonly used to make cement and binders chemically resistant. Wood adhesives, coatings, and explosive binders are among its numerous applications. The only downside of this material is that it is extremely harmful to human beings.
Vinyl Ester
This material is prepared by the combination of epoxy resin with vinyl acids. The vinyl acid is responsible for the cross-linking. Because of its qualities, it is commonly referred to as a hybrid of epoxy resins and polyester resins.
Vinyl Ester is resistant to water and corrosion, which is why it is commonly used in the marine industry. And because of its strong resistance to heat, it is used in chemical facilities and the petrochemical industry.
Polyester
It is formed by the reaction of a dysfunctional organic acid with polyhydric alcohol in the absence of a catalyst. Polyester can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to water and chemicals. Because of its strength and durability, it is used in the boat building industry to make several parts. Polyester is also applicable for making various electrical components, pipes, ducts, and tanks.
Properties of Thermosetting Polymers

Thermosetting polymers are distinct from other types of polymers; they have their unique properties. Below are the major properties of thermosetting polymers.
- Thermosets are heat resistant. But when the high intensity of heat is applied, they decompose before getting solidified.
- Once thermosets are solidified, they cannot be reformed or recycled.
- They have a 3-dimensional cross-linked molecular structure, which makes them very strong.
- The higher the crosslink density, the higher the toughness of the shape.
- Thermosets disintegrate when overheated.
- They are chemical resistant and can withstand both organic and inorganic acids.
- The density of thermosetting polymers is dependent on the constituent components.
- Thermosetting polymers remain stable at both high and low temperatures.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermosetting Materials
Just as with every type of polymer, thermosetting materials have their advantages and drawbacks.
Advantages
- Thermosetting materials are most suitable for high-heat applications, like electronics, and other equipment that are usually used under UV rays.
- They eliminate the risk of product melting when fierce heat is applied.
- Thermoset materials enhance resistance to heat and chemicals, which improves products structural integrity.
- They offer both thin and thick walls.
- Thermoset materials are preferable for wet-paste applications.
Disadvantages
- Once they are heated and solidified, they cannot be recycled, nor can they be reshaped.
- It is difficult to configure them into a specific surface finish.
Common Uses of Thermosetting Plastics
Because of their unique qualities, thermosets are extremely useful for improving the world and everyday lifestyle. Below are some of the uses of thermosetting plastics.
- They are used in virtually every industry to make permanent parts.
- Thermosetting plastics are used to make electrical appliances and components, including panels and insulators.
- Their uses also include making panels for construction equipment.
- Because they are heat resistant, they are commonly used to manufacture heat shields. Thermosetting plastics are used by medical practitioners in clean room molding.
- In the automobile industry, they are used to manufacture brake pistons.
- Thermosetting plastics are also used in agriculture for motors and feeding troughs.
Why Thermosetting Materials are so important for Injection Molding

All kinds of plastic can be used for injection molding, but thermosetting materials are very important because they can be used to manufacture permanent parts, whereas other materials like thermoplastics cannot do that. Thermosetting materials are so important for medical device injection molding that all the sectors of the world make use of them as they are resistant to many elements, such as electricity, water, chemical, heat, etc.
Also, they can be used to make any plastic injection mold design, but once the molding processes are completed, they cannot be changed or taken back to their previous state.
Conclusion
Depending on the application, there are numerous types of thermosetting plastic to choose from. In this post, we’ve discussed the major types, their advantages, drawbacks, and their applications. To make further inquiries or manufacture any permanent part, contact us, and we will be delighted to help.