Globalization is bringing about a new era in the manufacturing industry. Both injection molding and 3D printing are practical solutions among today’s manufacturers, such as plastic molding company, for creating intricate plastic components and parts.
Although both 3D printing and injection molding are excellent production techniques, they work best for specific tasks and are very distinct from one another. This is entirely dependent upon the customer’s needs. One can use these two methods for both production and quick prototyping. Since they both have advantages, one must first recognize the difference between injection molding vs. 3D printing to choose which would improve your client’s manufacturing process the most.
What Is Injection Molding?

Large items can be created using the manufacturing method known as injection molding. The process involves pumping molten materials into a mold. Usually, it is utilized as a mass-production technique to create thousands of similar goods. Although the technique is most frequently used with thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers, injection molding can also be applied with metals, glassware, elastomers, and sweets.
Many commonly used goods, such as syringes, plastic bottle tops, remote control casings, and other items, are produced using injection molding. When producing syringes, if your client deals with medical products, it is essential to always go for a reliable medical plastic injection molding company.
What Is 3D Printing?
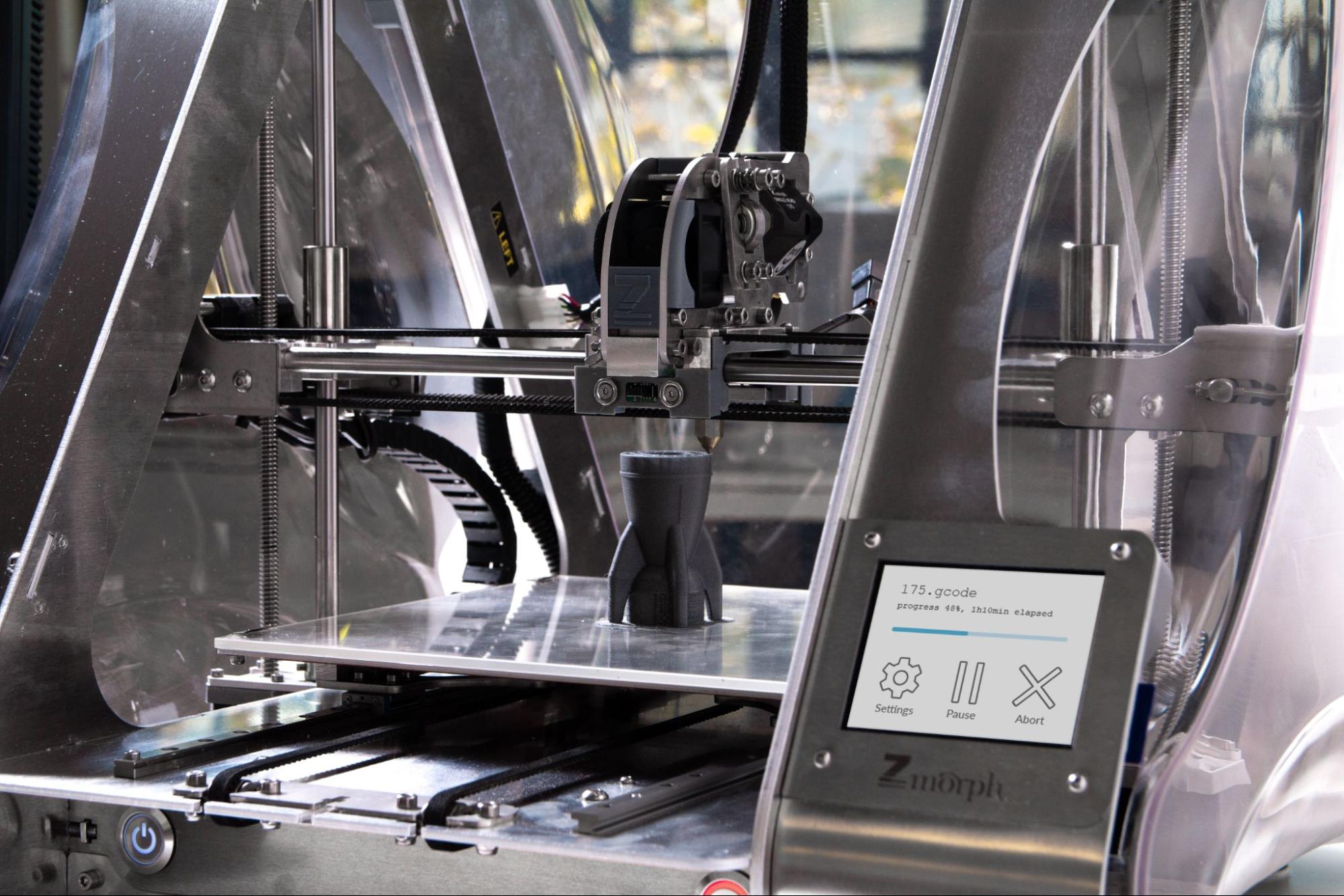

Making three-dimensional solid products from a digital file is known as 3D printing. In this process, an object is made by adding layers of material one after another until the product is made.
The healthcare sector is likewise seeing a 3D printing revolution. The COVID-19 epidemic in 2020 overran hospitals and heightened the demand for PPE kits. Many healthcare facilities used 3D printing to give their employees the protective gear they desperately needed and the parts to service their ventilators. In addition to revolutionizing PPE and medical equipment manufacturing, 3D printing will simplify implants and prosthetics.
Injection Molding Process
If one talks about the 3D printing vs. molding process, the fundamental objective of injection molding is to shorten the time required to prototype concepts, ideas, conceptions, and products. Before starting the project, careful planning is necessary to achieve that goal. The critical elements for each level are listed below.
- Mold closure (clamping): This applies tonnage while the mold closes. A mold is often divided into two sides: the A and B sides. There are numerous instances where it is possible to divide the mold into additional portions.
- Injection: Most molten plastic is pumped into the mold during this stage. The system is under pressure to fill the remaining mold gaps during packing and holding. When dealing with medical products, it becomes vital that the room is free of pollutants; clean room injection molding is always the best option.
- Cooling – The heated plastic is cooled to take on its final shape in this step. The cooling process can last a few seconds or several minutes.
- Mold Open: After a release of tonnage, the mold opens.
- Ejection: In this step, the part is removed to be sent or processed further. An injection cycle ends at this point, whether automatic or manual. The technique then continues from the clamping step onward for the subsequent sections.
3D Printing Process
In contrast to conventional techniques, 3D printing involves incredibly few stages, making it simpler to print. There are four processes:
Modeling
It is necessary to get a digital model of a 3D object before one may print it. Through modeling, individuals can create a digital version of the item they wish to print that can be used with a 3D printer. With the use of 3D modeling software, one can produce 3D models. In 3D printing, CAD (computer-aided design), and rapid prototyping, STL files are frequently utilized.
Slicing
After a model has been designed, it can be cut using specialized software. Slicing is a tool for the 3D printer to determine the path and quantity of filament needed to manufacture the model. The processes involved in construction and the required amount of wood must be calculated, just like when building a house.
Printing
Following the completion of the slicing, the slice file can be sent to the printer, where it can then be calibrated in advance of printing. It is necessary to calibrate the printing base and the extruders to increase printing accuracy and the user can have the quality assurance.
3D Printing Vs. Injection Molding Strength

Another vital issue to cover is 3D printing vs. injection molding strength. The question arises of which technique has more strength.
3D Printing Strength
3D printed objects are incredibly sturdy only when utilizing specialized filaments like Polycarbonate, which are used to make riot shields and bullet-proof glass. One can change the infill density, print orientation, and wall thickness to boost strength.
Injection Molding Strength
A single step is required to produce injection molded items instead of 3D printed parts, which may deteriorate where layers overlap. With injection molding, producing parts with repeatable tolerances of 0.500 mm is simple. Some applications even allow for the production of parts with tolerances as low as 0.125 mm, making them suitable for most applications. Since the parts are molded using heat, they are solid.
To summarize, 3D printing vs. injection molding strength, injection molding provides better strength.
3D Printing Vs. Injection Molding Disadvantages
3D printing disadvantages
3D printing is a slow manufacturing technique, even though the setup is quite quick. Most printers can only construct one or two objects at a time due to the CAD-based, exact procedure that limits the number of elements printed at once.
Larger objects cannot be created with 3D printing because the printing area’s size constrains the technique. While vast 3D printing is technically conceivable, this technology has better applications because the design becomes more unstable if sections hang off the border of the printing area.
Injection Molding Disadvantages
Because a mold is used, this production method is subject to some design restrictions. Removing the item without breaking or cracking it can be challenging. It is challenging and expensive to fix design errors because of the lengthy setup time frames involved with injection molding. That is why avoiding such mistakes is vital to always opt for an experienced medical plastics manufacturer.
The cost of injection molding equipment is high. These systems, which are intended for industrial usage, are not particularly suitable for hobby use because they incur additional costs beyond the machine’s purchase price for the creation of molds, prototyping, etc.
3D Printing Vs. Injection Molding Cost
If one manufactures more than 100 items, injection molding is more affordable than 3D printing. The price of injection molding improves considerably as one produces more components with the mold, while the cost per unit for 3D printing remains unchanged. Below is the detail about 3D printing vs. injection molding cost.
3D printing cost
As 3D printing becomes more widely available, many firms are now able to rationally evaluate the idea of buying a printer for in-house production.No matter how many copies need to be printed, the cost of printing a work will typically stay the same after it has been established. In some circumstances, 3D printing might be a less expensive option due to the low initial investment expenses. A project with fewer than 100 parts would be better suited for 3D printing.
Additionally, 3D printing is excellent for tasks requiring numerous revisions or when parts are required immediately. Additionally, 3D printing might be advantageous if the project is one-time and does not require continued production. The price of 3D printing can range from $3 to thousands of dollars. The cost of 3D printing depends on various elements, including labor, model complexity, and material.
Injection Molding Cost
Many crucial elements affect how much it costs to make a mold. These consist of the following:
- The item’s dimensions
- The item’s composition
- The product’s level of complexity
These three elements have the most significant effects on the overall investment sum needed to construct a mold. Based on these variables, the cost may range from $1,000 to more than $80,000.
To say that injection molding vs. 3D printing cost depends on different factors. 3D printing is affordable when one needs to print a few articles; however, injection molding is the choice when it comes to mass production.
Injection Molding Vs. 3D Printing Equipment
The various items required for these two distinct processes are listed below.
3D Printing equipment
3D Printer: Prices for 3D printers fluctuate widely. Several 3D printing services print the designs using various materials and equipment for people who do not have a printer.
Filaments: The 3D printer filaments are inserted into the printer. These filaments melt and are sprayed onto the printer’s bed to create the object.
Injection Molding Machine
Molding machine: An injection molding machine has an injection ram, material hopper, and a heating unit. These devices are made to keep the molds stationary while filling, ensuring that nothing moves them and tampers with the finished goods.
Molds: Molds are the most essential piece of equipment for injection molding. Since making molds from scratch is expensive, many manufacturers produce them in bulk to extend their budgets. They are typically constructed of aluminum, copper alloy, or hardened steel to withstand the heat process.
Injection Molding Vs. 3D Printing Application
3D printing and injection molding techniques produce extremely complicated parts for various sectors. Some of their applications are mentioned below:
Injection molding application:
Because of its adaptability, the injection molding method is used in every business sector, including the medical, aerospace, and automotive fields.
Medical: The medical device injection molding can produce parts equal to their metal counterparts in terms of high tensile strength and ability to withstand high temperatures. Additionally, this procedure enables low-cost production components, such as pill bottles, to produce orders in huge volumes. The customized injection molding allows the users to get the products according to their requirements. Injection molding can be helpful in the creation of sophisticated systems, such as those connected to X-ray equipment.

Construction: Due to the inherent versatility of plastic injection molding, many construction and building components are increasingly molded using this technique. Small and extensive accessories, fasteners, and other hand tools are some of the components that are most frequently produced in the construction sector.
Automotive industry: Plastic injection molded parts are widely used in the automobile sector due to their inherent design flexibility and excellent resilience and endurance. It is simple to design and construct various things with this technology, including bumpers, cup holders, mirror housings, etc.
3D Printing Application:

Education: More and more schools are adopting 3D printing techniques into their curricula daily. The advantages of 3D printing for education include better-preparing students for the future by enabling them to make prototypes without using pricey tooling.
Medical: The application for 3D printing and prototyping ranges from bioprinting to medical equipment like prosthetics.
Construction: Construction 3D printing offers several technologies that primarily employ 3D printing to fabricate buildings or construction-related parts.
Is Injection Molding Better Than 3D Printing
The debate goes around 3D printing vs. molding, so which one is better? For complex, small-batch products that may need frequent design modifications or customize, 3D printing is preferable. On the other hand, injection molding works better for mass-producing products after they have successfully finished the design phase. When it comes to injection molding vs. 3D printing, they both have specific uses.
Conclusion
Summing up, even though 3D printing has gained popularity recently, the majority of plastic parts for the industry are still made via injection molding. This is because regulating quality and costs is simple while still enabling mass output. If anyone is looking for a professional and reliable injection molding company, contact us for the best services and better deals.




