Plastic products are commonly used domestically and industrially. And this is because they possess so many properties, such as durability, lightweight, etc. Hence, over the years, the number of plastic molding companies has continually increased as all sectors are in great demand for plastic parts.
Using injection molding, which is a cost-effective method for producing large quantities of plastic parts, mass production is made to satisfy the high market demands. However, it’s expensive to set up the initial tooling and molds, which makes it less cost-effective for small production runs.
Other than these few points cited above, there are many other facts you need to know about the injection molding process.
What is Injection Molding
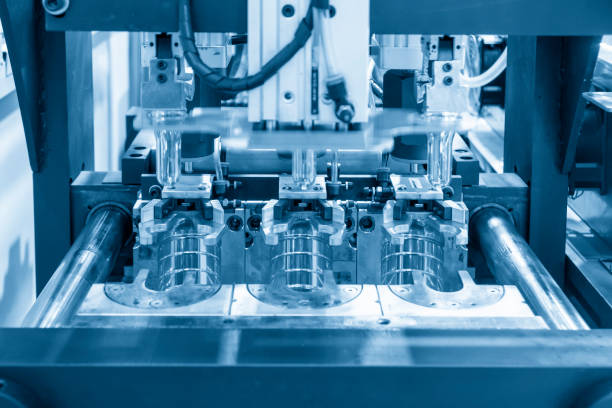
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic or other materials into a mold to create a specific product. It is one of the most widely used manufacturing techniques in the world and is used to create a wide range of products, from small consumer goods to large industrial parts. The process is also highly customizable, allowing for the production of complex geometries and precision parts with tight tolerances.
The injection molding process begins by heating plastic pellets or granules to a high temperature until they become a liquid. This liquid plastic is then injected into a mold under high pressure, where it is cooled and solidified. The mold is typically made of metal and is precision-machined to match the desired shape of the final product.
The History of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that was first patented in 1872 by John Wesley Hyatt, an American inventor. Hyatt was looking for a way to produce billiard balls using celluloid, a new type of plastic material that had been developed. He found that by injecting the celluloid into a mold, he could produce billiard balls quickly and efficiently.
The process of injection molding was further developed in the early 20th century by various inventors and companies. In 1946, American inventor James Watson Hendry built the first screw injection machine, which allowed for more precise control of the injection process. This led to the development of more advanced injection molding machines that could produce a wider range of products.
In the 1950s and 60s, injection molding became a popular method for producing a wide range of consumer products, such as toys, household items, and appliances. The process was also adopted by the automotive industry, which used it to produce parts such as dashboards and door panels. Even the medical molding companies joined as they started using the method to make plastic medical devices like syringes, tubes, surgical instruments, etc.
In the following decades, injection molding technology continued to advance, with the development of new materials, such as engineering plastics and bio-based plastics, as well as new manufacturing techniques, such as multi-component molding, in-mold decoration, and micro-injection molding. Today, injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that is capable of producing a wide range of products with high precision and efficiency.
Types of Injection Molding
There are several types of injection molding, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. They include:
- Thermosetting Injection Molding: In this process, a thermosetting plastic is used as the raw material. The plastic is heated and then injected into a mold. Once it cools and solidifies, it cannot be remelted. This type of injection molding is typically used for creating parts that require high strength, such as electrical components or industrial equipment.
- Thermoplastic Injection Molding: In this process, a thermoplastic material is used as the raw material. The plastic is heated, melted, and then injected into a mold. Once the part cools and solidifies, it can be remelted and recycled. This type of injection molding is commonly used for consumer goods and medical components manufacturing, as well as other products that require a high degree of precision.
- Co-Injection Molding: This process involves injecting two different materials into a single mold simultaneously. This allows for the creation of parts with unique properties, such as a harder exterior and a softer interior. Co-injection molding is commonly used for creating products such as grips for tools, and other products that require a combination of strength and flexibility.
- Micro Injection Molding: Micro injection molding is a specialized form of injection molding that is used to create small, precise parts. The process is similar to standard injection molding, but the machinery is designed to handle very small amounts of material and produce parts with extremely tight tolerances. Micro injection molding is commonly used by medical plastic manufacturers for creating small medical components. This process is also used for producing electronic parts, miniature parts for toys, and other consumer goods.
- Insert Molding: In this process, a pre-manufactured insert is placed into a mold before the injection process begins. The insert can be made of a variety of materials, including metal, plastic, or glass. Once the molten material is injected into the mold, it surrounds and bonds to the insert. This process is commonly used for creating products such as handles, knobs, and other items that require a combination of different materials for optimal performance.
- Overmolding: This process is similar to insert molding, but instead of placing a pre-manufactured insert into the mold, a previously molded part is used as the insert. The new material is injected and bonds to the existing part. This process is commonly used for creating products such as grips for tools, and other products that require a combination of strength and flexibility.
- Two-Shot Injection Molding: In this process, two different materials are injected into a mold in two different steps. This allows for the creation of parts with unique properties, such as a harder exterior and a softer interior. Two-shot injection molding is commonly used for creating products such as grips for tools, and other products that require a combination of strength and flexibility.
Injection Mold Tooling
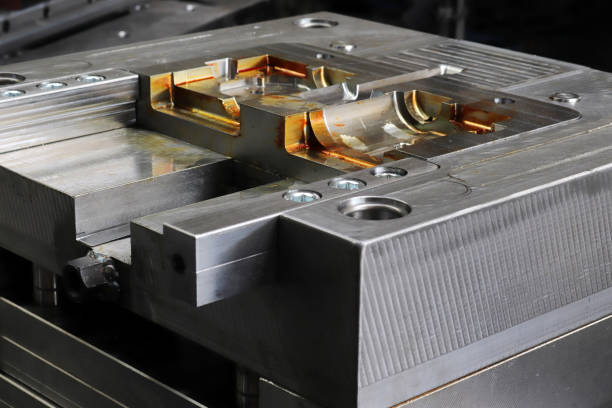
The mold, also known as a tool or die, is a hollow cavity that is the negative of the part being produced. The mold is typically made of steel or aluminum and is precision-machined to the desired shape of the final product.
The tooling used in the making the mold is a critical component that plays a major role in the production of high-quality, accurate parts. However, the design and development of injection molding tooling can be complex and challenging.
One of the major complexities in injection molding tooling is the design of the mold itself. The mold must be able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the injection process, as well as the thermal expansion and contraction that occurs during cooling. Additionally, the mold must be able to maintain precise tolerances and produce parts with consistent dimensions. This requires a high level of engineering expertise and experience in materials science.
Another complexity in injection molding tooling is the process of creating the mold itself. The process typically involves the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a 3D model of the desired part. This model is then used to create the mold, which can be made from a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, and even ceramic. The choice of material can have a significant impact on the overall performance of the mold, so it is important to select the right one for the specific application.
Additionally, the development of injection molding tooling can be costly. The cost of the tooling can vary greatly depending on the size and complexity of the part, as well as the material and process used to create the mold. This can make it challenging for companies to justify the investment in tooling, especially for small or one-time production runs.
Injection molding tooling also requires regular maintenance to ensure that it continues to function properly. This includes cleaning, lubrication, and replacement of worn or damaged parts. Failure to properly maintain the tooling can lead to poor quality parts, increased downtime, and higher production costs.
To make a perfect injection mold, it requires a high level of expertise and experience in materials science, engineering, and computer-aided design. However, with proper design and development, the use of injection molding tooling can result in high-quality, accurate and cost-effective parts for a variety of applications.
Materials Used in Injection Molding
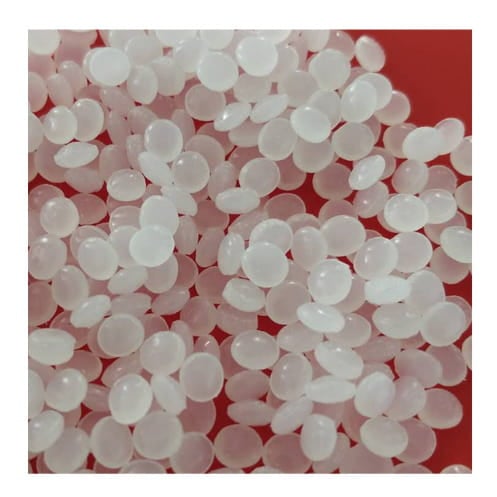

The materials used in injection molding can vary depending on the application, but the most commonly used materials include thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers.
Thermoplastics
A type of plastic that can be melted and re-melted multiple times without losing their properties. They are widely used in injection molding because they can be easily molded into a variety of shapes and sizes.
Some common thermoplastics used in injection molding include:
- Polyethylene (PE): is a lightweight and flexible material that is often used to make bottles, containers, and other packaging materials. It is also commonly used in the manufacturing of toys and household goods.
- Polypropylene (PP): is a strong and durable material that is often used to make automotive parts, such as battery cases and fuel tanks. It is also used in the manufacturing of household appliances and furniture.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): is a strong and flexible thermoplastic that is known for its resistance to chemicals and water. It is commonly used in piping, electrical cable insulation, and medical device injection molding.
- Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS): is a strong and durable thermoplastic that is known for its resistance to impact and chemicals. It is commonly used in automotive parts, electronic housings, and toys.
- Polycarbonate (PC): is a strong and transparent thermoplastic that is known for its resistance to impact and high temperatures. It is commonly used in safety glasses, electronic housings, and medical equipment.
- Acetal (POM): is a strong and stiff thermoplastic that is known for its low friction and wear resistance. It is commonly used in gears, bearings, and electrical components.
- Nylon (PA): is a strong and durable thermoplastic that is known for its resistance to impact and high temperatures. It is commonly used in gears, bearings, and automotive parts.
Thermosets
Thermosetting plastics are a type of plastic that solidify and harden when heated, and cannot be remelted. These materials are known for their high strength and durability, and are often used in applications where high strength and dimensional stability are required.
Some common thermosetting plastics used in injection molding include:
- Polyester: is a strong and durable material that is often used to make automotive parts and appliances. It is also used in the manufacturing of electrical components and other industrial goods.
- Epoxy: is a strong and durable material that is often used to make electrical components, as well as in the construction industry for adhesives and coatings.
- Phenolic: is a strong and durable material that is often used to make electrical components, as well as in the manufacturing of gears and other mechanical parts.
Elastomers
Elastomers are a type of rubber-like material that are known for their flexibility and elasticity. They are often used in injection molding to create flexible parts, such as seals and gaskets.
Some common elastomers used in injection molding include:
- Polyurethane (PU): is a flexible and durable material that is often used to make seals and gaskets, as well as in the manufacturing of footwear and other consumer goods.
- Nitrile Rubber (NBR): is a strong and durable material that is often used to make seals and gaskets, as well as in the manufacturing of automotive parts and other industrial goods.
- Silicone: is a flexible and durable material that is often used to make seals and gaskets, as well as in the manufacturing of medical devices and other consumer goods.
Injection Molding Process
The injection molding process is simple with following these steps:
- The design of the product should be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- The plastic material, typically in pellet form, is then loaded into the injection molding machine.
- The plastic is heated and melted until it reaches a liquid state.
- The molten plastic is then injected into the mold tool under high pressure.
- The mold tool is cooled, typically with water, to solidify the plastic.
- Once solidified, the product is ejected from the mold tool.
- The process is repeated as needed to produce multiple copies of the product.
- Once the products are made, they are inspected for defects and then packaged for shipping.
How does an Injection Molding Machine Work
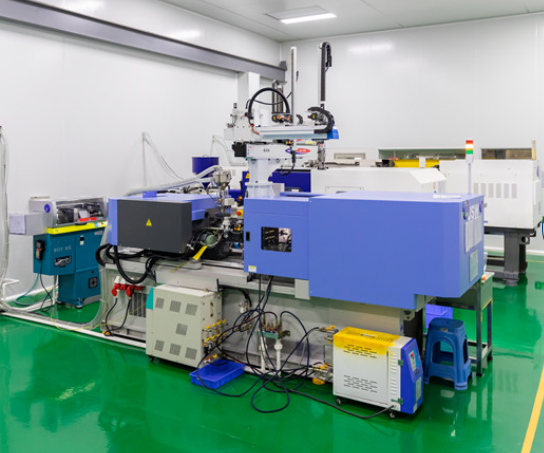

An injection molding machine includes a hopper for the plastic pellets, a heating barrel where the pellets are melted, a screw that injects the molten plastic into the mold, and a mold clamp that holds the mold shut during the injection process. The machine also includes controls for adjusting the temperature, pressure, and speed of the injection process.
The machine works by heating plastic pellets until they become a molten liquid, which is then injected into a mold under high pressure. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens and the part is ejected. The process is repeated to produce multiple parts.
What Products are made from Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce a wide variety of plastic parts and products. Some common examples of products made using injection molding include:
- Medical equipment (e.g. syringes, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment).
- Automotive parts (e.g. dashboards, door panels, and interior trim).
- Electronic devices (e.g. phone cases, tablet housings, and computer components).
- Household items (e.g. toys, kitchen utensils, and containers).
- Industrial components (e.g. gears, bearings, and machine parts).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Molding
Thanks to injection molding, many industries can produce products in large volumes, including products with tough geometries. The advantages benefitted from this process are many. However, it still has some shortcomings.
Advantages
- High production rates: Injection molding machines can produce large numbers of parts quickly and efficiently.
- Repeatability: The process is highly repeatable, meaning that parts produced using the same mold will be very consistent in terms of shape and size.
- Complex geometries: Injection molding can be used to produce parts with complex geometries and intricate details.
- Materials versatility: A wide variety of materials can be used in injection molding, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
- Customization: Injection molding offers flexibility and ease of customization. And for sectors like the medical industry, clean room injection molding is done to produce health devices that are not harmful to the human body.
Disadvantages
- High initial costs: The cost of creating a mold can be quite high, especially for complex or detailed parts.
- Limited design flexibility: Once a mold has been created, it can be difficult or expensive to make significant changes to the design of the part.
- Environmental effect: The process requires a significant amount of energy and generates a significant amount of plastic waste, which can be an environmental concern.
- Material waste: Injection molding can result in significant material waste, as any material that is not injected into the mold is discarded.
- Finishing: Additional work may be required on the molded parts to have the desired finish.
Defects that Happen in the Injection Molding Process
There are many potential defects that can occur in the injection molding process, including:
- Flash: A thin layer of excess plastic that forms along the edge of the mold.
- Warping: The deformation of the plastic part as it cools and solidifies.
- Short shots: When the plastic does not fill the entire mold cavity.
- Sink marks: Indentations on the surface of the part caused by uneven cooling.
- Weld lines: Visible lines on the surface of the part where two streams of plastic have met but not fused together.
- Bubbles: Air trapped in the plastic during the injection process.
- Burn marks: Discoloration or charring of the plastic caused by overheating.
- Ejector pin marks: Small marks on the surface of the part caused by the pins used to eject the part from the mold.
- Knit lines: Visible lines on the surface of the part where two layers of plastic have fused together.
- Incomplete filling: When the plastic does not fill the entire mold cavity due to lack of pressure or improper gate design.
How to Prevent Injection Molding Defects
There are several ways to prevent defects in the injection molding process. They include:
- Proper design of the mold: A well-designed mold can help prevent defects by ensuring that the plastic flows evenly and completely fills the mold cavity.
- Proper machine set-up: Ensuring that the injection molding machine is set up correctly, including the correct temperature and pressure settings, can help prevent defects.
- Proper material selection: Selecting the appropriate plastic material for the part, taking into account its intended use and the conditions it will be exposed to, can help prevent defects.
- Proper process control: Monitoring and controlling the injection molding process, including the temperature, pressure, and speed of the plastic as it is injected into the mold, can help prevent defects.
- Quality control: Regularly inspecting parts for defects and making adjustments to the process as necessary can help prevent defects from occurring.
- Proper Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the injection molding machine and mold tooling can ensure that the equipment is running optimally and prevent defects.
- Properly trained operator: A well-trained operator can ensure that the machine is properly set up and the process is running smoothly, which can help prevent defects.
Factors to Consider When Finding Injection Molding Manufacturers

When considering a custom plastic injection molder, there are several factors to consider. They include:
- Quality and capability: The manufacturer’s track record of producing high-quality parts and the ability to meet your specific requirements and specifications.
- Capacity and lead time: The manufacturer’s production capacity and lead time, and the ability to meet your production and delivery schedule.
- Cost: The cost of the manufacturer’s services, including the cost of the mold and the cost per unit for the parts.
- Location and logistics: The location of the manufacturer and the logistics of getting the parts to you, including shipping and customs costs.
- Equipment and technology: The manufacturer’s equipment and technology, including the type and age of the machines, and their ability to produce parts with tight tolerances or complex geometry.
- Experience and expertise: The manufacturer’s experience and expertise in your specific industry or application, and their ability to provide technical support and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
- Quality control: The manufacturer’s quality control processes, including inspection, testing, and certifications.
- Communication and responsiveness: The manufacturer’s ability to communicate effectively and respond to your needs in a timely manner.
- Flexibility and scalability: The manufacturer’s ability to adjust production to meet your changing needs and scale production as your business grows.
- Reputation and references: The manufacturer’s reputation and references from previous clients can provide insight into their reliability, quality, and customer service.
Choose the Best Plastic Injection Mold Manufacturer
Globally, Seaskymedical is highly-rated and has proven to be the best plastic injection mold manufacturer. Having a great specialty in carrying out injection molding in a clean room, they supply quality and reliable plastic molded parts for various industries.
Seaskymedical focuses on the development and production of plastic injection molded products, offering assistance in all stages, including product design and development, mold design and development, material selection, and injection molding.
Would you like to make any injected mold and product? Contact us today and enjoy the best services!