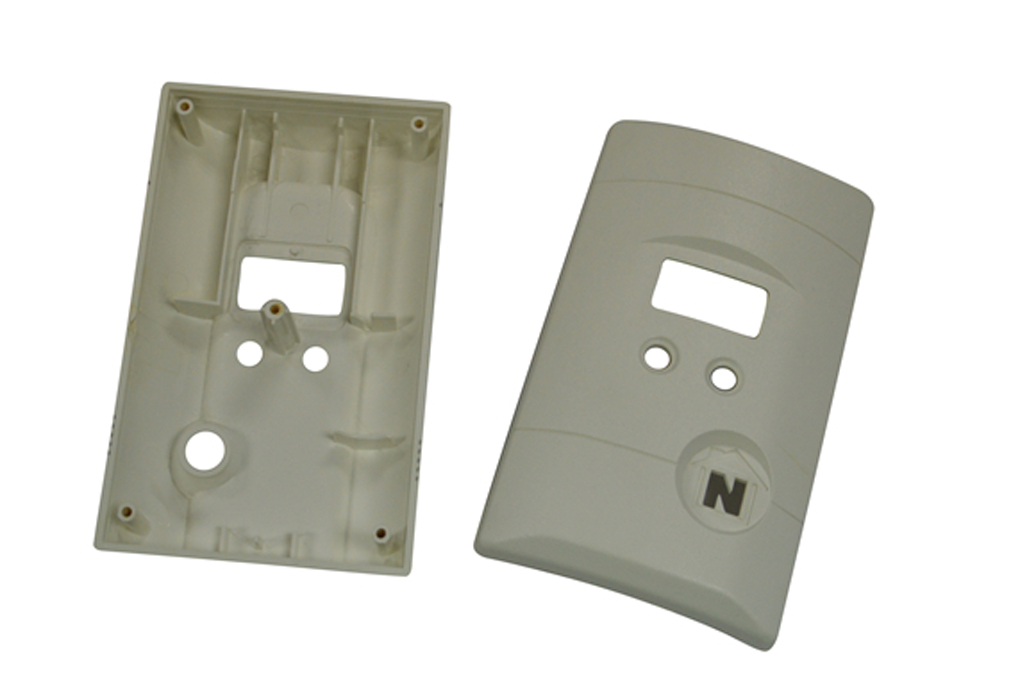
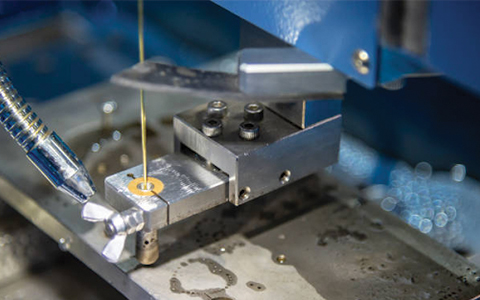
Injection molding is the most popular method for manufacturing parts, and it’s used in various industries, such as aerospace, food & beverage, automotive, and medical industries. Its several applications are because of the numerous benefits it provides, which includes, the manufacturing of more parts in less time and the capability to manufacture extremely complex parts.
But how does this method work and how different is it from other methods?
In this post, you will find out as we will be discussing everything you need to know about injection molding, starting from what it is, then defining the different types like what is plastic injection molding, and so many other things. Now, let’s dig in!
What is Injection Molding

Injection molding is a manufacturing method that involves injecting molten materials into a mold for it to cool and solidify. It is used to make thousands of identical parts, which enables the large-scale production of items. Materials used in injection molding include plastics, metals, rubbers, and elastomers. Although plastic materials, thermoplastics and thermosets are most frequently used.
Injection molding is a very versatile method that allows for the combination of several materials and finishes, making it a popular choice in many sectors, even those that have different aims and objectives.
Also, the unique process of manufacturing parts using injection molding allows you to make intricate parts with detailed designs, which is not something that can be easily achieved with other molding methods.
What are the Types of Injection Molding
There are different types of injection molding processes and their usage depends on the type of part you want to make. Described below are the various types that exist. Knowing them will help you know exactly what you want when you seek a molding injection company.

Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is the most common type of injection molding. It has to do with injecting molten plastic resins into a mold, letting it cool, solidify, and take the shape of the mold. It is used to produce a wide range of items, ranging from car and airplane components to storage containers, medical items, musical instrument parts, hair combs, etc.
Plastic injection molding uses a lot of plastic resins, such as polystyrene, polyethylene, acrylic, polycarbonate, and polypropylene.
Micro Injection Molding
Micro injection molding is a high-precision molding method that’s used for manufacturing small parts and components. This method is used in several companies, such as the medical molding company for the making of surgical equipment and other applications. It’s also used in electronics and other industries, where smaller equipment are preferable. However, this method is one of the most difficult injection molding methods as the materials used always have large molecules by nature, but now, they need to be configured into small dimensions.
While a tight tolerance is required in all injection molding methods (Learn: Solving the Injection Molding Shrinkage with Effective Ways) , more attention must be paid to micro molding because even the smallest dimensional fluctuation can destroy your whole hard work.
Overmolding
Overmolding is sometimes called 2-times molding as it involves the molding of an already molded part. It allows you to make a part out of two or more polymers.
This method is usually used when a manufacturer discovers that a part’s production can be improved by using different materials. Also, it’s used when you need a better grip on a part, such as molding a plastic or elastomer resin on a metal part. Overmolding items are typically used for everyday applications, such as personal care products or tool accessories.
Insert Molding
Insert molding involves the encapsulation of a previously manufactured component in molten material in order to produce a strong and beautiful finished part. The insert component is usually a basic item like a knife, blade, or surgical tube. And in some cases, it could be as sophisticated as a battery or motor.
This injection molding type is perfect for increasing a part’s strength and reliability while also reducing cost and production time by eliminating the need for additional production like soldering and adhesives.
Cube Molding
Cube molding is also called rotating cube molding or stack-turning molding. The cube molding method is characterized by parts that rotate vertically round an axis. While manufacturing, the mold’s lower section runs on the machine base and the lower machine tie bars. While the upper section of the part runs on the top machine tie bars. This type of injection molding is specifically suitable for manufacturing circular plastic parts.
Die Casting
Die casting is a metal casting method in which molten non-ferrous alloys are poured into dies at high temperatures and speed to produce molded items quickly. It is very suitable for manufacturing parts with complex geometries. The most common materials used for die casting are aluminum, zinc, magnesium, lead, and copper.
It can be used for different purposes, such as medical devices, outdoor lighting, traffic lights, firearms, telecommunications, etc.
Gas-assisted Injection Molding
The problem with any thick plastic injection-molded item is that when it cools, it may deform. But the gas-assisted injection molding helps to prevent this by injecting gas into a plastic material-filled injection mold. This allows the outside of the mold to have a smooth appearance while the inside remains porous and hollow. This method does not only prevent the item from deforming during the cooling period, but it also reduces the total cost as you will be using less material.
This method is suitable for items that require a hollow part as they will be fabricated without incurring additional costs.
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding type has to do with using an injected material for a hot mold to manufacture a part. Then after this, a cold material is injected to make it flexible in terms of parts without having to re-expose itself to high heat.
This method is particularly useful for high-quality medical items and automobile parts. It is not suitable for hot temperatures, but its process necessitates the use of extremely hot molds.
Metal Injection Molding
In addition to plastics, injection molding uses a number of other materials, and one of them is metal. This is one of the new technologies displacing traditional methods as some industries need very complex parts that cannot be made from plastic.
Industries that deal with metallic parts can also make use of injection molding in manufacturing needed parts. This is especially useful for digital purposes in the electronics and other manufacturing industries.
Reaction Injection Molding
This injection molding type simply involves the mixing of two different types of materials at very high pressure in an impinging mixer. After they’ve been perfectly mixed, they are then injected into the mold at a lower pressure.
Thin-wall Injection Molding
This is an advanced type of injection molding that results in a plastic object with a very thin wall. This method is very useful if you want to reduce the cracks on the molded part. It holds the highest level of precision since it is usable for small parts.
To ensure that the thin wall geometry will stand without compromising quality, each aspect of the mold design, part design, and processing should be carefully evaluated. This method is often used in tubes, test apparatuses, vessels, electronics, and other enclosures.
RJG Injection Molding
This is a reference to RJG, a firm based in the United States that created a mechanism for evaluating the plastic injection molding process in order to improve control. This method is also known as decoupled molding, which means separating the molding process into a particular fill, pack, and hold sections of the process. It is applicable to hot runner systems, particularly on older machines.
How Does Injection Molding Work?

The very first step in injection molding is the creation of the mold as that’s the shape the part will result in. Most molds are finely machined from metal, usually aluminum or steel to match the features of the product they are to manufacture.
After the mold has been made, the material needed for the part is poured into a heated barrel and mixed thoroughly. The material is then melted by heating bands, and the molten material is fed into the mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies to take the shape of the mold. Mold tools are mounted on the plate molds, which open once the material is solidified so that the ejector pin would remove the part from the mold.
Meanwhile, separate materials can be combined to make one part; this is called a two-shot mold. This technique is used to add a soft touch to molded parts, add colors to parts, or manufacture parts with different performance characteristics. Also, molds can be made to be of single or multiple cavities. Each cavity of a multiple cavity mold can have identical parts or be unique to generate parts with diverse geometries.
Due to the injection and clamping forces, aluminum molds are not recommended for high-volume manufacturing or products with tight dimensional tolerances since they have poor mechanical qualities and are prone to wear, distortion, and damage. While steel molds last longer than aluminum molds, they are more expensive.
The shape and features of the part, the materials for the part and the mold, and the properties of the injection molding machine must be carefully designed for the injection molding process to be a success.
What is Injection Molding Process?
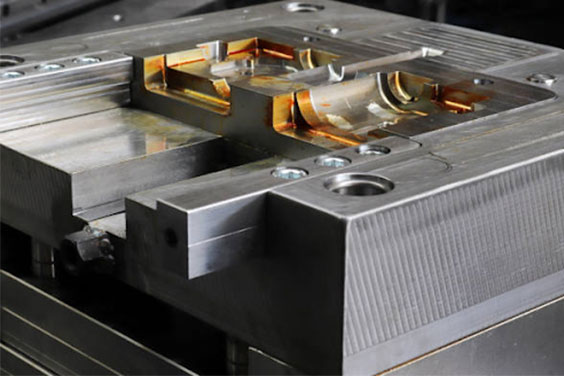
Below is a step-by-step process involved in injection molding.
- Selecting the right material for products and mold: This is essential as the material and the mold must be compatible if the injection molding process will be successful. This is because some types of materials are not suitable for some mold designs.
Before the final mold design is made, tools should be made and tested using Computer Assisted Design (CAD) and 3D printing technologies. These tools should be tested with the right material to ensure that the molded part would have the right properties.
- Feeding and melting the thermoplastic: The thermoplastic material of your choice is fed into the hopper at the top of the injection molding machine. This material is gradually transmitted into the machine’s barrel as the screws rotate. As the screw turns and heat is generated from the barrel, the thermoplastic material gradually melts until it is completely molten.
Maintaining the right temperature at this stage is very important as it ensures that the plastic material is injected properly and the final part is formed accurately.
- Injecting the plastic into the mold: When the molten plastic reaches the end of the barrel, the gate that controls the injection of plastic closes and the screw moves back. This draws a certain amount of plastic through the screw, preparing it for injection. When the tool and screw are at the proper pressure, the gate opens, the screw advances, and the molten plastic gets injected into the mold.
- Holding and cooling time: After injection into the mold, the molten plastic is held under pressure for some time, which is known as “holding time.” It varies depending on the type of thermoplastic, however, it ranges from milliseconds to minutes.
After the holding time, the screw retracts, allowing the part to cool in the mold; this is known as “cooling time.” The timing also varies, but it’s usually between some seconds to some minutes. This makes sure that the part sets properly before being ejected and finished on the production line.
- Ejection and finishing processes: After the holding and cooling period have been completed, pins or plates are used to eject the part from the tool. Then, the parts are dropped into a chamber or onto a conveyor belt at the machine’s bottom. Finishing operations like polishing, dying, or removing extra plastic may be needed in some situations, but these can be done by other machinery or operators.
What Materials are Commonly used in Injection Molding
There are several materials that are used in injection, but shortly, we will be discussing the most common ones i.e., the injection molding materials that are usually used more often.

Polyethylene (PE)
PE is the most popular injection molding material for a lot of applications, such as milk bottles, toys, plastic bags, medicine, detergent bottles, etc. Polyethylene is a low-cost material with excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and electrical insulation. It isn’t particularly strong or durable, but it is very much affordable.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a high-performing material with a low melting point that makes it simple to work with. This is an opaque material that can be combined with colorants, which come in several textures and surface finishes. It is known for its strength and resistance to external forces.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a tough, impact-resistance material that is characterized by low shrinkage and dimensional stability. It is a transparent plastic that comes in a variety of optically clear grades and has a high cosmetic finish as well as an outstanding heat resistance.
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
It’s also known as “acetal.” This material is extremely hard, stiff, and tough. POM has strong lubricity and is resistant to hydrocarbon and organic solvents. It must also be mentioned that it has good elasticity and slipperiness.
Polyamide
Polyamide is also called ‘nylon.” There are numerous types of polyamide and each of them have their benefits. However, in general, polyamides have high strength, thermal tolerance, and are resistant to chemicals except for acids and bases.
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
PMMA is also called “acrylic.” It provides good optical qualities, high gloss, and is resistant to scratch. And for geometries with thin sections, it offers low shrinkage and reduced sink.
Polypropylene (PP)
This is a low-cost injection molding material that has great impact resistance, although it can be fragile in extremely freezing temperatures. Also, polypropylene is resistant to wear and can provide high elongation, as well as being incredibly resistant to acid and base.
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
This high-temperature, high-performance material is resistant to heat and retards flame. Also, it has great strength and is very stable dimensionally, as well as being resistant to chemicals.
Advantages of Injection Molding

The major advantage of injection molding is being able to boost production by manufacturing an increased number of parts within a period of time. And once the initial cost of design and molds has been covered, the cost of production reduces. This is because a lesser amount of money is spent with the increase in parts produced.
Also, when compared to the traditional production method i.e. CNC mold making, injection molding produces less waste. Regardless, injection molding produces waste, primarily from the gate locations, sprue, runners, and any overflow material that spills out of the part cavity.
Finally, it enables the manufacturing of multiple identical parts, ensuring part uniformity and reliability in high-volume production.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding has a high upfront cost, especially when it comes to tooling. A prototype tool and part would have to be produced and tested before any real part is made. And this process takes a lot of time and money, which is why so many industries are seeking for competent injection mold tooling suppliers to help them manufacture ready-made molds in order to fasten the injection molding process.
Also, injection molding isn’t suitable for making large parts in one piece. This is because of the size constraints of injection mold machines and tools. If at all large items must be made with injection molding, they are to be made in many parts and joined together afterwards.
Lastly, only professionals can make large undercuts without making a mistake and causing additional cost.
Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding prioritizes precision and cost-effectiveness, which is what most industries are looking for. This is the reason why the manufacturing process is applied in several industries. Below are some of the industries that use injection molding.
Food and Beverage
As previously stated, injection molding allows industries to manufacture parts from several materials. And that’s very important in the food & beverage industry, where you need to comply with numerous laws regarding the safety of food containers. With injection molding, you can use non-toxic and BPA-free polymers that are both safe to come in contact with food and can also withstand high and low temperatures.
Building & Construction
With custom-made and sophisticated plastic parts playing important roles in the building & construction industry, injection molding has become a necessity. And in many cases, parts used in building & construction must also meet some stringent rules in terms of quality. For example, when making parts for windows and doors, the parts must not only be great, they must also last longer and be able to withstand environmental factors.
Medical & Pharmaceuticals
Medical plastic injection molding manufacturers are now able to produce vital tools and parts because of the low-cost involved in injection molding. And this has also boosted the success of clean room injection molding as more people all over the world can now afford quality healthcare. Many essential medical equipment, such as monitors, syringes, and heart pumps rely on injection molding’s precision, making the manufacturing method indispensable in this industry.
Automotive Parts
Many of the modern autos can function properly unless they are composed of some intricately designed parts. As a result, many of the automobile industry’s top executives have resorted to injection molding to design, plan, and manufacture parts that are needed. Examples of these parts include dashboards, bumpers, and smaller parts like cup holders and mirror housings.
Household Products
There is a considerable possibility that you’ll find an injection molded part in every household that you go to. Like other industries, household items are more affordable when they are made through injection molding and this has boosted the rate of production over the years. Examples of household items made with injection molding are cups, food containers, and other kitchen utensils.
Agriculture
Formerly, the agriculture industry has a habit of investing in metal-made components simply because they last longer. But due to improved plastic material properties, such as UV resistance, humidity resistance, and impact resistance, reinforced plastic are preferred. Because injection molding can be used to manufacture more durable agriculture parts that can withstand the elements on the farm, it has become an apparent choice. Examples of injection molded parts for agriculture are feeding troughs and specialized harvesting components.
Mold in Injection Molding

A mold is a hollow metal block into which molten material is injected to make a specific shape. This is one of the most important elements in injection molding as the design of the mold determines the shape the part will take. The molten material is injected into the mold, where it cools, solidifies, and takes the shape of the mold. After this, the mold is opened and you have your molded part.
What Factors should be considered in Injection Molding
There are quite some factors that are needed to be considered before undertaking injection molding as they will help to make the injection molding process faster and easier.

- Cost: The startup cost for injection molding can be high, so you have to seriously consider the total cost you will incur.
- Material cost: This is determined by determining the weight of the materials needed and the unit price. The material weight includes the material used to fill the mold’s channels. The thickness of the part determines the size of the channels, and thus the number of materials needed.
- Production cost: This is computed by the hourly rate and the cycle time. Because the hourly rate is linked to the size of the injection molding machine in use, it’s necessary to understand how the part design influences machine selection.
- Mold Tooling cost: Also, the total amount that will be incurred on the mold tooling i.e., the mold base and the machining of the cavities should be considered. It can be reduced in many ways, including eliminating undercuts, using a multi-cavity, using a core cavity approach, etc.
- Mold Tooling Design: The design for injection molding tools should also be considered. This is because an accurate mold tooling design guarantees that there is no defect during production.
- Production Quantity: Before beginning the injection molding process, you should consider the number of parts you want to manufacture as injection molding is mostly suitable for large production quantities as the total cost will be reduced.
- Production Considerations: Production will be improved by using cycle time and using machines with hot runner molds and well-thought tooling. Such little changes and the use of hot runner systems can result in significant cost savings for your parts. Minimizing assembly requirements will also save money, especially if you’re producing tens of thousands or millions of parts.
- Uniform Wall Thickness: Another factor you need to put into consideration is the wall thickness of the parts. They should be uniformly molded to avoid additional cost or production time.
- Injection Molding Machines: These are the components of an injection molding machine.
- Injection unit: This unit is in charge of heating and injecting the material into the mold.
- Clamping unit: this is the unit that is responsible for opening and closing the two halves of the mold.
- Control: Another factor to be considered is how the mold will be controlled during the injection molding process. Ensure that all the needed items are available for seamless control.
- Base: One other part of the injection molding machine to consider is the mold base. This is because the mold core and cavity are both fixed to the mold base, which is then attached to the injection molding machine’s platens.
What Do Injection Molding Manufacturers Do
The capabilities and services offered by injection molding manufacturers differ. Some manufacturers solely work with pre-existing designs, while others assist in the part production. However, this is a list of what injection molding manufacturers do.
- Part design
- 3D rapid prototyping
- Mold tool design
- Mold tooling making
- Injection molding production
- Pad printing
- Assembly
- Packaging & hot sampling
- Distribution
Conclusion
Injection molding is referred to as the most popular manufacturing method not just because it is cheap, but because it is applicable to all the industries including medical device molding, electronics, agriculture, food & beverage, building & construction, etc.
Also, it is widely used because it’s the best method when large quantities of identical parts are to be produced.
While other manufacturing methods are good at what they do, none is yet to come close to injection molding.