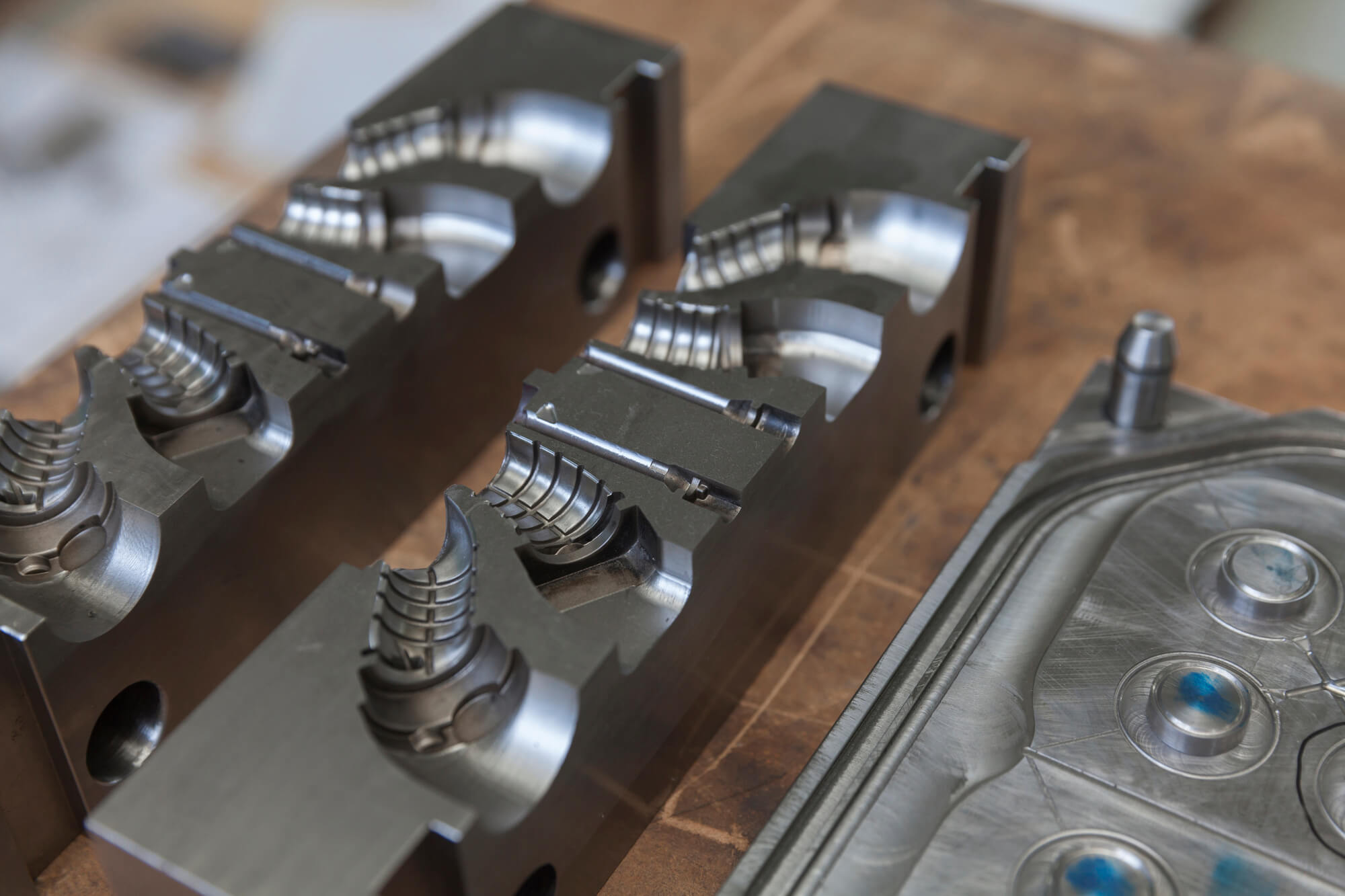
When you are considering manufacturing methods for metal parts, an option that cannot be left out is die casting. This is because it provides the broadest range of shapes without sacrificing their tight tolerance. Die casting is also considered a great choice because it’s cost-effective and it involves the implementation of efficient technologies.
In this post, we will explore this incredible manufacturing method, starting from what is die casting, its history, types of machines used in executing it, the processes involved, the ideal metals for this purpose, and so many more.
What is Die Casting

Die casting is a metal manufacturing method that entails the forcing of molten metal material into a mold cavity under high pressure. This method is used to manufacture complex geometries. However, it can only be used with non-ferrous metal i.e., metal materials that don’t contain iron. Examples are aluminum, zinc, magnesium, lead, and copper.
For die casting to be carried out, four essential elements are needed. They are:
- Mold which is also known as die
- Die casting machine
- Metal material
- Furnace
The metal material is melted in the furnace, then the liquid is injected into the mold in the die casting machine. After this, it will cool and form the shape of the mold.
The History of Die casting
The invention of die casting dates back to the early 1800s when the first die casting machine was used in the printing industry. This technological innovation was beneficial at the time as it boosted the creation of mobile products.
Later in the year 1849, Sturges was awarded a patent for the invention of the first small hand-operated machine for casting printing type. His invention was one-of-a-kind. The machine was created to produce a wide range of simple to complex shapes while maintaining a high level of accuracy, and consistency.
In 1855, Otto Mergenthaler, another inventor, designed the linotype machine, which quickly became popular and efficient equipment in the printing industry.
Later in the 19th century, due to the increased volume of production in numerous industries, there was a significant need for commercial die casting. This increase in demand allowed the die casting industry to enlarge its reach and penetrate new markets. It was during these early days that Aluminum and Zinc became largely used, rather than Tin and Lead which were originally used. Aluminum and Zinc were preferred because they produce higher quality products.
Also, formerly, low-pressure injection die-casting was used, but now, high-pressure casting method is employed. This is because it provides improved surface finishing and more efficient production factors.
Throughout history, die casting processes have been used to make all major items notwithstanding the complexity of their shapes. This saves firms a significant amount of money during the manufacturing process and improves their production rate and quality.
What are the Types of Die Casting Machines
There are three different types of die casting machines. They are hot chamber die casting, cold chamber die casting, and vacuum chamber die casting. They are unique and are used in different applications.
Hot Chamber Die Casting

Hot chamber die casting machines are sometimes called gooseneck machines. They are most suitable for metal materials that have low melting points. Examples are zinc, magnesium, and lead alloys. These metal materials are heated and melted in a furnace that is attached to the hot chamber die casting machine. After this, they are transferred into the die directly through goosenecks.
A distinctive feature of hot chamber die casting machines is that the casting chamber is continually in contact with the liquid alloy. The molten metal enters the casting chamber through a valve, where the piston forces it into the closed die casting mold at high speed.
Advantages
Hot chamber die casting has numerous advantages. Some notable ones are:
- Guarantee of high production rate, particularly when multi-cavity dies are used.
- Faster production cycling time.
- Ease of using a casting machine to melt the metal.
- Better productivity and surface finish.
- Dimensional tolerances are very tight.
- Production of complex shapes with thin walls.
- Due to the lower melting points of metal materials, a longer lifespan is guaranteed.
Disadvantages
Despite the numerous advantages of hot chamber die casting, there are still some limitations. They include:
- Only metals with low melting points are suitable. This is because the components of the casting machine are always in direct contact with the molten metal.
- It is ideal for producing only small castings that weigh less than 4.5 kg.
Cold Chamber Die Casting

Cold chamber die casting machines are designed in a way that the casting set is separate from the furnace where the metal material will be melted. This machine is most suitable for metal that has high melting points. Examples are aluminum, copper, and brass alloys.
The process starts with melting the metal in an external furnace, and an amount is ladled through a pouring hole into the shot chamber, which has a ram that drives the molten metal into the die. After the metal has been poured into the die, it solidifies under the high pressure, whereupon you can now open the latches of the die, and eject the casting alongside the gate and slag of excess metal.
Advantages
- With cold chamber die casting, you can produce large parts weighing as much as 20 kg.
- Great success will be recorded if it’s used to cast metal with high melting temperatures, such as aluminum, copper, brass, and zinc-aluminum alloys.
- You can easily use cold chamber die casting to make metal parts with intricate shapes.
Disadvantages
- When compared with hot chamber die casting, it requires a longer cycle-time. This is because you will have to transfer the molten metal from the furnace to the cold chamber machine.
- It requires an auxiliary system for pouring the molten metal into the casting chamber.
Vacuum Die Casting

Owing to the several limitations of the other types of die casting machines (hot chamber die casting and low chamber die casting), vacuum die casting was developed. It is a more advanced version of the other types of die casting.
Vacuum die casting is a high-pressure die casting supported by a vacuum pump that’s used to remove the air trapped within the die cavity, which is why it’s also called vacuum-assisted high-pressure die casting. It’s used to avoid the several casting defects that occur in the other types of die casting. As a result, die casting manufacturers who want higher quality metal parts make use of it.
Vacuum die casting can be used for both hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting.
The processes involved in vacuum die casting machines are identical to the other types of die casting machines except that vacuum is created during this process. Below are the major processes involved in vacuum die casting:
- The metal material will be melted. If you’re using a cold chamber machine, you will have to melt the metal alloy in a separate furnace. If you are using a hot chamber machine, the melting of the metal alloy will be done with the machine.
- Move the molten metal into the shot chamber. In hot chamber machines, a plunger is used for this purpose, but in cold chamber machines, a ladle is used.
- Afterwards, a vacuum is created and metal injection under high pressure will be carried out.
- The air in the die cavity will be eliminated, allowing the molten metal to reach all the parts of the die uniformly.
Advantages
- Production of higher quality metal parts.
- It reduces surface defects and eliminates the need for other surface finishing.
Disadvantages
- It is expensive.
What are the Die Casting Process Steps
The steps taken in die casting vary depending on the preference of the manufacturer. However, these are the 6 major die casting process steps that manufacturers take.
- Die preparation: Firstly, the die needs to be prepared for casting. To do this, it is sprayed with either a lubricant or a releasing agent. To make this easy, the lubricating substance is combined with water which evaporates when sprayed on the hot steel die. This process is done to enable smooth release after the metal part is completely casted.
- Clamping: Clamp the die halves together with high pressure. The amount of force to be used is determined by the machine.
- Injection: The metal alloy is melted and poured into the clamped die with high pressure. The high pressure holds the molten metal in the die until it cools. Injection time is dependent on the complexity of the metal parts – wall thickness, multiple patterns, and internal caverns.
- Cooling: Once molten metals are injected into the die, they start cooling. The type of metal used, temperature, and the complexity and wall thickness of the metal parts determine how long this process will take. During the process of cooling, the die cannot be unclamped. When the metal is finally cooled, it will take the shape of the die.
- Ejection: After metal parts are completely cooled, the die halves are unclamped and an ejection mechanism removes the molded metal parts. Monitor the force used to remove the metal parts to avoid damages.
- Trimming: This is the final die casting process step. While the metal materials are cooling, oftentimes, there are excess metal materials in the sprue and runner. They must be removed, as well as any flash (a thin metal around the edge of your molded metal parts) that has occurred. The extra materials that are attached to the final casting are trimmed off, recycled, and reused in the die casting process.
What are the Most Common Metals Used in Die Casting
The same rule of “material selection” applies to every fabrication industry i.e., the quality of the material selected determines how good the final product will be. Just like how you need to ensure that you make the right decision in your plastic material selection for injection molding, so also must you select the right metal material for die casting.
There are different metals from which you can choose for your die casting project. Below are the most common metals used in die casting.
Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum is one of the favorite metal options used in die casting. It is a light metal suitable for making lightweight parts without compromising strength. It’s easy to cast and it provides better finishing options.
Aluminum is an extremely corrosion-resistant metal that contributes to the increased longevity and safety of components. In addition, the toughness and the strength-to-weight ratio are unrivaled.
Zinc Die casting
Like aluminum, zinc is among the favorite metals used in die casting. It’s also commonly used for automotive and medical device molding. Because zinc has a low melting point, it requires less energy to produce. Its low melting point also helps to lengthen equipment life, which is why most companies like a medical plastic injection molding company will prefer using it.
Zinc castings are often the greatest option for customizing products for aesthetic reasons. Depending on the application, the material can be plated or painted. It also provides a nice working surface. Zinc enables fabricators to create components with bespoke aesthetic quality.
Magnesium Die casting
Magnesium is very easy to machine. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio and is the lightest die cast alloy available.
Magnesium alloys have a number of advantages over other cast metals. Some of those advantages are good fluidity, less sensitivity to hydrogen porosity, and improved castability.
Bronze and Brass Alloys
Bronze and brass are malleable alloys, allowing them to be molded into a variety of shapes and forms, regardless of how complex they are. Because of these metals’ dimensional accuracy and flexibility, die casted parts can be made in large quantities.
When compared to other metal casting and forging methods, die casted equipment made with bronze and brass alloys have good dimensional tolerance, material integrity, and surface polish.
Lead Alloys
Lead alloys are specially used for metal parts that need close dimensional accuracy and are highly resistant to corrosion. They are commonly used for fire safety equipment, bearings, and numerous decorative metal objects. Although lead alloys are quite affordable and commonly used, they are not suitable for products that will come in contact with food.
Copper
In general, copper alloys have a high level of corrosion resistance, making them a good choice for long-term cost efficiency. Copper also has the highest mechanical properties of alloy die cast, which makes them applicable in several applications.
Other benefits attributable to this metal are high hardness, outstanding wear resistance, good dimensional stability, and high strength almost like that of steel parts.
Silicon
Silicon is amongst the common metals used in die casting and this is because it provides high strength and serves as an alternative investment for cast steel parts. Its strength makes metal parts very strong and resistant to external factors.
Which Material is Best for Your Application
Different applications are suited for different metals. So, the metal that is best for your application is determined by the purpose of the metal parts. For instance, if you need a metal part or molding method like insert molding solutions that can withstand high temperature, then your first consideration will be aluminum. But you need to keep in mind that aluminum can only be die casted with a cold chamber machine.
If you need a lightweight metal, you will first consider magnesium as it’s the lightest of all metals used in die casting. Also, you need to remember that lead alloys cannot be used for equipment that will come in contact with food.
Basically, the material that is best for your application is dependent on your specificity and your need, such as electrical & thermal conductivity, hardness & strength, harsh environmental stressors, and extreme temperature. To make a better decision on the material to use, you might need to contact a fabrication company.
What is Die Casting Used for
Die casting has various material options and design flexibility, which makes it applicable to several industries. Die casting is used for several purposes by many industries. Some of them are:
Medical devices
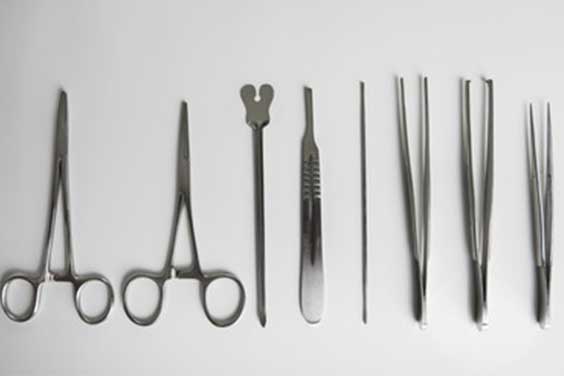
Die casting is usually used to make medical devices as most of them are made from aluminum, which is a metal material. Examples of die casted medical devices are surgical tools, monitors, operating room robots, and gear boxes for hospital beds. They are usually manufactured and assembled in a clean room for medical devices because they need to be contamination-free.
Outdoor lighting and traffic lights

Lighting enclosures and other parts for traffic lights can be made using aluminum alloys and casting dies. This metal is cheap and lightweight, and it’s a good conductor with excellent thermal properties.
Firearms

Most of the parts of shotguns, pistols, and rifles can be made of die cast metal. Some of the die cast metal parts are triggers, trigger guards, and safeties.
Manufacturing Factory

You can’t walk far within the perimeters of a manufacturing plant without finding a few die casted parts. This ranges from air compressors and wall mount bearing housings to industrial pumps, piston connecting rods, and porter cable pump housings.
Telecommunications

The telecommunication industry as well depends greatly on die cast aluminum parts because of their high conductivity, low weight, and longevity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting
Advantages
- Increased production speed in relation to other manufacturing methods.
- Accurate dimensions.
- Requires little or no machining.
- Metal parts produced from die casting are Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) shielded.
- Suitable for metal parts with difficult geometry.
- In the long run, it’s cost-effective.
- Wastage of material is reduced.
- Improved strength and weight for thin-wall castings.
Disadvantages
- The initial capital is high.
- There will be porosity if the air in the die cavity is not completely emptied.
- Ferrous metals cannot be used.
What is Die in Die Casting
A mold is also referred to as a die in die casting.
Adie is one of the specialized tools used in the die casting process. It’s made of hardened steel that is machined and designed to the net shape or close to the net shape of the part that’s to be made.
In die casting, two dies are required. The first is the “cover die” and the other is the “ejector die.” Where these two dies meet is called the dividing line. The ejector pins and the runner, which is the passage from the shot hole to the cavity, are commonly found in the ejector pin. The molten metal flows into the dies through a sprue or shot hole in the cover die.
Factors that Affect Die Casting Costs
Below are the basic factors that influence the cost of die casting.
- Metal material: One of the major elements necessary for die casting is metal materials, such as aluminum, zinc, copper, lead, and silicon. Before starting your die casting process, you need to estimate the amount of money you will spend on buying the metal materials you need.
- Equipment: The equipment used in die casting processes are usually expensive. This is one of the downsides of die casting. You will need to invest a large sum of money in acquiring your die casting machine, which like other machines, is liable to depreciate and get damaged.
Die casting process requires high pressure injection of molten metal into the die casting machine which is liable to erode during the manufacturing process, thereby losing its sharp edges. With time, it stops producing intricate details and as time goes on, it will need frequent maintenance or replacement, which translates to additional cost.
- Labor: The labor involved in die casting is not much, however, the total cost involved must be estimated and put into consideration.
Injection Molding vs. Die Casting

Injection molding and die casting are both fabrication methods that are used by manufacturers to make components. However, there are some differences between them. Quickly, we will examine the differences between these two fabrication methods – injection molding vs. die casting.
Process Comparison
There is a great disparity in the material and process used in injection molding and die casting.
In injection molding, plastics or polymers are used as raw materials, but in die casting, metal materials are used.
There are 4 steps in the injection molding process. They are: mold preparation, injection, cooling, and ejection.
For die casting, there are 6 steps. They are: die preparation, clamping, injection, cooling, ejection, and trimming.
Mold Comparison
These are the differences in the molds used for injection molding and die casting.
- The mold required for die casting is usually constructed to be stronger and thicker than the mold used in injection molding. This is because the molten metal injected into die casting molds are usually at high pressure.
- A single mold is used for injection molding, while die casting requires two molds. The mold used in die casting is divided into two halves; the first is called the “cover mold” and the other, “ejector mold”.
- The mold used for injection molding does not require clamping, while the molds used for die casting needs to be clamped before the molten metal is injected.
Advantage Comparison
Another set of differences exist in the advantages.
Advantages of Injection Molding
- Injection molding is cheaper. The cost incurred in plastic injection molded parts is not expensive.
- The injection molding process is more flexible.
- It accommodates the combination of several plastic materials, which makes overmold injection molding possible.
- Fillers can be used to strengthen plastic molds.
- Plastic injection molding parts are capable of insulating electricity.
Advantages of Die Casting Advantages
- Ensures a higher accuracy and tighter tolerance.
- It can be used to make complex shapes.
- Die casted parts are stronger and more heat resistant than plastic injection.
- High speed production.
- Die casted parts have smoother surfaces.
Conclusion
Die casting is a thriving sector of the manufacturing industry. It’s a process that’s been used in numerous industries to make metal parts with diverse shapes, including complex shapes. When compared with other manufacturing processes, die casting has a high speed production rate, and produces high quality and accurate components.
For your die casting needs, you can contact Seaskymedical for the perfect guidance and execution of projects.




