The automotive industry has been increasingly utilizing various types of plastics to manufacture car components, thanks to their lightweight, durable, and versatile properties. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of automotive plastic materials and their uses, while also discussing the evolution of plastics in automotive engineering, how to choose the right type of plastic for your automotive parts, and the role of sustainability in auto manufacturing.

Introduction to Types of Plastics Used in Cars: A Brief Overview
Automotive plastics are widely employed in the manufacturing of various car components, including both exterior and interior car parts. The most commonly used automotive plastics include:
| Plastic material | Checklist |
| Polypropylene (PP) | ☑️ |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | ☑️ |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | ☑️ |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | ☑️ |
| Polyurethane (PUR) | ☑️ |
| Polyethylene (PE) | ☑️ |
| Polyamide (PA/Nylon) | ☑️ |
| Polystyrene (PS) | ☑️ |
| Polyoxymethylene (POM) | ☑️ |
| Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | ☑️ |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | ☑️ |
| Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA) | ☑️ |
Each of these plastics offers unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications in the automotive industry. You can see the Injection Molding Materials selection here. From lightweight construction and fuel consumption efficiency to increased safety and comfort, these materials have revolutionized the way cars are designed and manufactured.
The Evolution of Plastic in Automotive Engineering
Car companies have been using plastics since the 1800s. At first, they only used plastics for simple parts. But since the 1950s, plastics have been used to make many car parts. Today, a normal car has between 40 to 100 kg of plastic parts. Even though plastics make up only 10% of a car’s weight, they are important.
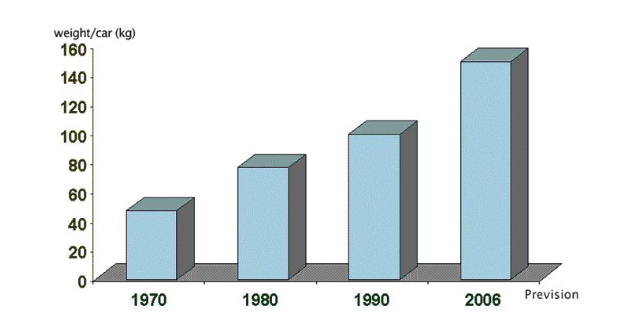
As people want lighter, more efficient, and eco-friendly cars, automotive OEMs are making new plastics and ways to use them. Now, plastics are used for things like bumpers, doors, fenders, and interiors.
Plastics started as basic parts but now enable key trends in car design:
- Weight loss. Plastics weigh less than metals, so using them can make cars 50% lighter. Lighter cars need less fuel and pollute less. For every 10% less weight, fuel use goes down 5-7% and emissions drop a lot.
- Lower costs. Plastic materials and molding cost less than metal parts. So, plastics lower how much it costs to make cars.
- Styling. Plastics can be shaped in more ways, so they allow for sleeker, more stylish car designs.
- Safety. Plastics absorb more impact in a crash. Parts like bumpers and door panels protect riders better. New plastics for windows and body panels also boost safety.
- Eco-friendly. Plastics make cars more sustainable by improving efficiency and using renewable materials. Recycled and bio-based plastics are better for the environment.
- New technology. Plastics enable new features like self-driving cars, connectivity, and alternative power. Plastic parts can add sensors, electronics, and new other materials to build the cars of the future.
Plastics have transformed how cars are designed and made. They have huge potential for making higher-quality, cheaper, and more sustainable vehicles. In the future, plastics may replace more metal parts, enabling more progress in efficiency, safety, technology, and style.
Finding the Ideal Plastic Material for Car Components
Selecting the high performance plastics for your automotive depends on several factors, including cost, availability, mechanical properties, and compatibility with the desired manufacturing process. Here is a quick overview of the common types of automotive plastics and their typical applications:
Polypropylene (PP)

Plastic polypropylene (PP) offers superb resistance to chemicals and is nearly impermeable to water. Among polypropylenes, black grades provide the greatest resistance to ultraviolet light degradation. Due to these properties, PP sees widespread use in the automotive and construction sectors. Common automotive applications of polypropylene include:
- Bumper Fascias
- Gas Cans
- Engine Covers
- Cable Insulation
- Instrument Panels
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)

PVC is renowned for its ability to withstand impacts and resist damage from chemicals and solvents. Its vinyl composition provides strong tensile strength, and some PVC grades are flexible. PVC comes in both colored and transparent varieties. It is often used for interior plastic automotive parts such as:
- Dashboards
- Door panels
- Upholstery underbody protection
- Vehicle airbags
Polycarbonate (PC)

Polycarbonate possesses superior resistance to environmental exposure and UV radiation, approaching the optical transparency of acrylic. Its lightweight enhance vehicle efficiency and fuel economy.
Application:
- Car bumpers
- Headlight lenses
- Bullet-proof glass
- Security screens
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)

ABS plastic is an extremely durable, thermoformable plastic that can withstand harsh weather and some chemical exposure. Though rigid, it has enough flexibility to provide shock absorption. This makes it ideal for applications where impact resistance and durability are critical, like vehicle components designed to protect passengers.
Application:
- Dashboards
- Wheel covers
- Body parts
Polyurethane (PUR)

Polyurethane is a versatile, insulative, and moldable plastic. It is also suitable for making parts that require strength and resilience.
Application:
- Car seats
- Headrests
- Soundproofing systems
- Car bumpers
- Tires
Polyamide (PA/Nylon)
Nylon is a strong and heat-stable plastic that is commonly used for heavy-duty applications in automotive manufacturing.
Applications:
- Engine covers
- Door handles
- Gears
- Fuel caps
Polystyrene (PS)

Polystyrene is a naturally transparent polymer that has excellent heat resistance properties.
Application:
- Car interiors
- Knobs
- Fittings
- Door panels
- Sound-dampening foam
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is a durable, chemical-resistant, and lightweight plastic that is commonly used for making plastic fuel tanks and glass-reinforced vehicle bodies.
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
The plastic POM is renowned for retaining its shape, withstanding exposure to chemicals, and resisting damage from ultraviolet light. Due to these properties, POM is commonly used to construct automotive components that demand high tolerances and durability when exposed to fuels, harsh chemicals, and low temperatures. Applications include interior and exterior trim pieces as well as fuel system components.
Polycarbonate (PC)

Polycarbonate has good weather and UV resistance, with transparency levels almost good as acrylic.
Application:
- Car bumpers
- Headlamp lenses
- Bullet-proof glass
Acrylic (PMMA)

Acrylic is more transparent than glass, has a reasonable tensile strength (shatterproof grades are available) and good UV and weather resistance, high optical quality, and a surface finish with a huge color range.
Application:
- Automotive topcoats
- Car light covers
- Motorcycle windshields
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
PBT plastic has excellent chemical and electrical resistance. It is a hard, tough material that absorbs little water. PBT can withstand dynamic stresses and maintains dimensional stability even in extreme heat. It is easy to process due to its fast crystallization and cooling properties.
Some common applications of PBT include:
- Electrical plug and connector housings: PBT’s chemical and electrical resistance make it suitable for these applications.
- Bumpers: PBT’s durability, toughness, and stress resistance allow it to absorb impacts without damage.
- Door handles: PBT’s hardness, dimensional stability, weather resistance, and ease of processing make it ideal for automotive door handles and other trim components.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)

PET plastic shares many of the useful properties of PBT, such as good thermal stability, electrical resistance, and low water absorption. It also has excellent surface finish characteristics.
Some common applications of PET include:
- Automotive body panels: PET’s durability, weather ability, and surface appearance make it suitable for vehicle body panels and trim.
- Engine covers: Under-hood components like engine covers require plastics that can withstand high heat over long periods of time, so PET is a good choice.
- Electrical connector housings: Like PBT, PET’s chemical and electrical resistance make it a good insulator for electrical connectors and components.
- Headlamp retainers: PET’s strength, dimensional stability, and temperature resistance allow it to securely retain headlamps in place despite vehicle operation in a wide range of environments.
Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA)
Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA) is an extremely tough, rigid plastic with excellent chemical and heat resistance. It has outstanding durability against weathering, aging, and yellowing, and can be produced with a high-gloss finish.
Some applications of ASA include:
- Instrument panels: ASA’s rigid yet impact-resistant nature, along with its resistance to environmental factors like heat and UV light, make it suitable for automotive instrument panels.
- Vehicle interiors: ASA’s durability, aesthetics, and processing ease are ideal for various interior trim components.
- Electrical components: ASA’s chemical resistance and thermal stability allow it to insulate and protect electrical parts even in hot, harsh environments.
Greener Vehicle Production: How Bioplastics Enable Sustainability
As environmental concerns continue to grow, the automotive industry is increasingly focusing on the use of sustainable materials, such as bioplastics. Bioplastics are derived from renewable resources, such as plants, and are designed to biodegrade when exposed to natural environmental conditions.
Some examples of bioplastics used in the automotive manufacturing process include:
- Polylactic Acid (PLA): This bioplastic is derived from corn starch and is commonly used for packaging and disposable cutlery. In the automotive industry, it is used for producing interior trim components and exterior body panels.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): PHA is a family of biodegradable plastics produced by bacteria. They are used for making automotive parts, such as airbags, seat covers, and dashboard components.
- Bio-based Polyurethane (Bio-PU): This bioplastic is derived from plant oils and is used for producing foam components, such as car seats and headrests.
The use of bioplastics in automotive manufacturing not only reduces the industry’s dependency on fossil fuels but also contributes to more sustainable and eco-friendly production processes.
Conclusion
The automotive industry has increasingly adopted plastics over traditional materials like metal in vehicle design and manufacturing. Plastics offer many benefits such as reduced weight, improved fuel economy, enhanced safety features, and a more comfortable driving experience. In addition, as environmental sustainability has become more important, bioplastics made from renewable materials have emerged as an alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
By selecting from the range of plastics available, automakers can choose the optimal materials for each vehicle component. Whether looking to improve fuel efficiency, enhance safety, or provide a superior driving experience, plastics have enabled automotive innovation. To obtain high-quality plastic components for your automotive needs, contact seaskymedical.